
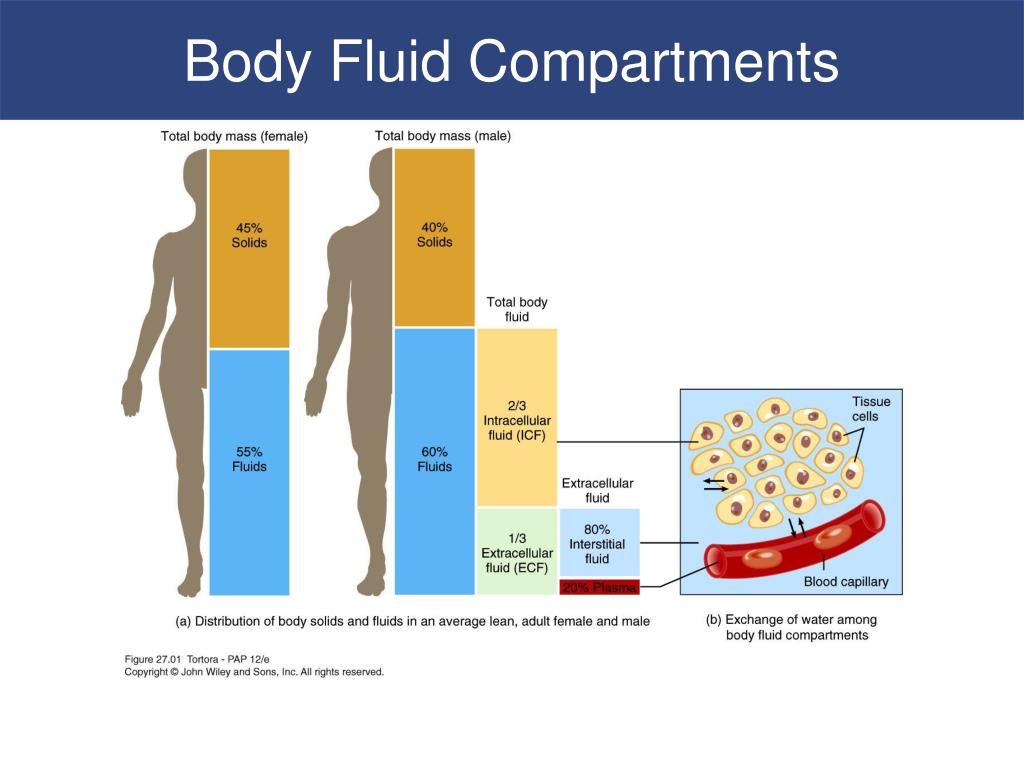
And that our normal reference range for sodium is 135 to 145.Īnd finally, our interstitial compartment is our tissue compartment. And it’s important to know that our normal, our primary cation inside of the intravascular compartment is sodium. Our intravascular compartment is actually all of the other fluid within that vessel that is not inside of cells, right? All of the plasma, the plasma proteins like albumin, all of the additional fluid inside of these vessels is our intravascular compartment. And it’s important to know that our primary cation inside of the cells is potassium with a normal reference range of 3.5 to 5.1. That’s our first fluid compartment, our intracellular compartment, it’s the fluid inside of the cell. This is the way that we’re going to conceptualize these three different compartments, right? Our intracellular compartment is actually the fluid inside of the cell. And within that blood vessel, we have all of these little red blood cells. So what we have here is a hand and we’ve got an arm and inside of this arm, just like yours and my arm, we have blood vessels. Let’s actually bring a little bit of clarity and make this make sense. And the third is our interstitial compartment. The second is going to be our intravascular compartment (excuse that spelling). The first one that we’re looking at is our intracellular compartment. So whenever we’re talking about fluid compartments, we are pretty much looking at three primary fluid compartments, and I’m gonna break these down a little bit. I really want to discuss the various types of compartments where fluid can reside within our body, as well as how fluid moves interchangeably between these various compartments. And in today’s video, we’re going to discuss our fluid compartments. Hey guys, my name is Brad and welcome to. Diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane from an area of low concentration of solutes to high concentration of solutes.Movement of particles using a transport channel/protein or carrier molecule.Movement of particles through a semipermeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.Other particles or substances require facilitated diffusion.Only certain small particles and water can pass through.All fluid spaces are separated by some sort of semipermeable membrane.Particles which are dissolved in a solution.Liquid in which particles are dissolved or carried.A substance containing both a liquid (solvent) and particles (solutes).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
